プロジェクトのご紹介 10 - Project 10 -
IL-21 によるアレルギー応答の制御とその分子機構
IL-21-mediated regulation of allergic responses and its molecular mechanisms
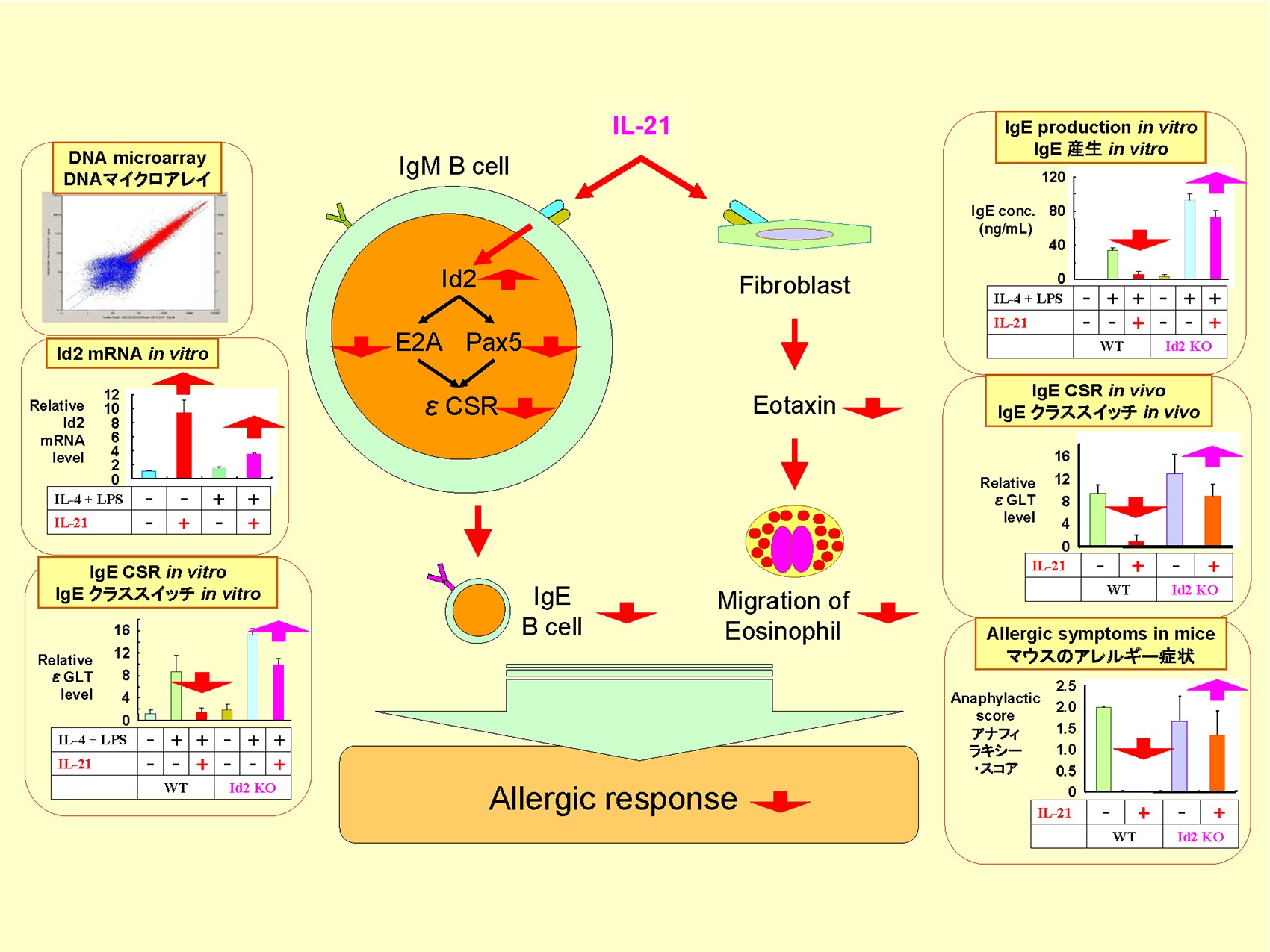
IL-21 シグナルは、B 細胞の IgE クラススイッチを抑制するという報告がなされていたが、
矛盾する報告もあり、IL-21 シグナルが IgE クラススイッチの抑制に関与する分子機構は明らかでなかった。
一方、アレルギーを発症する個体内における IL-21 の in vivo の作用も知られていなかった。
我々は、IL-21 が転写制御因子、Id2 を誘導し、Id2 が必須に関与して IgE クラススイッチを抑制することを見出した。
IL-21 はまた、線維芽細胞に働いてエオタキシン産生を抑制し、好酸球のアレルギー局所への遊走を抑制した。
さらに、アナフィラキシーおよびアレルギー性鼻炎を誘導したマウスにおいて、アレルギー症状を強力に抑制することを見出した。
これらの結果は、IL-21 がアレルギー病態の制御に有用である可能性を示している(Kishida et al., J Immunol; Hiromura et al., J Immunol)。
Some earlier reports suggested that IL-21 signal prevented B cells from undergoing IgE class switch recombination (CSR),
but other reports were inconsistent with this view.
Involvement of IL-21 signal in the regulation of IgE CSR was not clarified at molecular level.
It was also unveiled whether exogenous IL-21 plays some role in vivo in animals that show manifestations of allergic diseases.
We found that IL-21 provoked B cells to express the transcriptional regulator, Id2,
which was essential and sufficient for the IL-21-induced suppression of IgE CSR.
IL-21 also acted on fibroblasts and inhibited production of Eotaxin,
so that the eosinophil infiltration into the allergic lesion was significantly hampered.
Moreover, IL-21 strongly alleviated allergic symptoms in mice that otherwise exhibited systemic anaphylaxis or allergic rhinitis.
These results strongly suggest that IL-21 may be feasible for controlling allergic disorders
(Kishida et al., J Immunol; Hiromura et al., J Immunol).
一部プロジェクトのご紹介 - See some projects among others -
- 新型コロナウイルス・オミクロン変異株に対する茶カテキン類の効果
Effects of tea catechin-related compounds on Omicron subvariants of SARS-CoV-2 - 腫瘍微小環境の低pHはプロトンセンサーGたんぱく共役レセプターをを介して腫瘍のPDL-1の発現を低下させる
Extracellular acidity in tumor tissue upregulates programmed cell death protein 1 expression on tumor cells via proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptors - 緑茶カテキン、カテキン誘導体、およびガレート型テアフラビンによる新型コロナウイルスの試験管内での有意な不活化;紅茶と緑茶による試験管内での唾液中の新型コロナウイルスの迅速な不活化
Significant Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by a Green Tea Catechin, a Catechin-derivative and Galloylated Theaflavins in vitro; Rapid Inactivation in vitro of SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva by Black Tea and Green Tea - 新規多孔性3Dスキャフォールドと直接誘導骨芽細胞を用いた骨再生
Nanogel tectonic porous 3D scaffold for direct reprogramming fibroblasts into osteoblasts and bone regeneration - TGFR阻害剤による骨芽細胞のケミカル・ダイレクト・リプログラミング
Chemical direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts into osteoblasts by a TGFR blockade - 筋芽細胞のダイレクト・リプログラミングと筋管形成
Direct reprogramming of functional myoblasts that are capable of forming multinuclear myotube - シュワン細胞のダイレクト・リプログラミングと末梢神経損傷の再生
Direct reprogramming of functional Schwann cells that promote regeneration of peripheral nerve - 褐色脂肪のダイレクト・リプログラミングと代謝疾患の制御
Direct reprogramming of functional brown adipocytes that control metabolic diseases - 骨芽細胞のダイレクト・リプログラミングと骨再生
Direct reprogramming of functional osteoblasts that regenerate bone tissue - IL-21 によるアレルギー応答の制御とその分子機構
IL-21-mediated regulation of allergic responses and its molecular mechanisms - IL-27 による NK 細胞活性化と ADCC を介した腫瘍抑制
IL-27 augments NK cytotoxicity and induces ADCC-based tumor suppression - EBV- エピゾーマルベクターによる外来遺伝子の高効率導入、高発現、長期間持続の機構解明
Mechanisms underlying the high-rate transfection, high-level expression, and long-term maintenance of exogenous genes mediated by the Epstein-Barr virus-based episomal vector - 細胞の分化と初期化に伴う染色体エピジェネティック修飾の解析
Analyses of epigenetic modification of chromosomes upon cell differentiation and reprogramming