プロジェクトのご紹介 8 - Project 8 -
褐色脂肪のダイレクト・リプログラミングと代謝疾患の制御
Direct reprogramming of functional brown adipocytes that control metabolic diseases
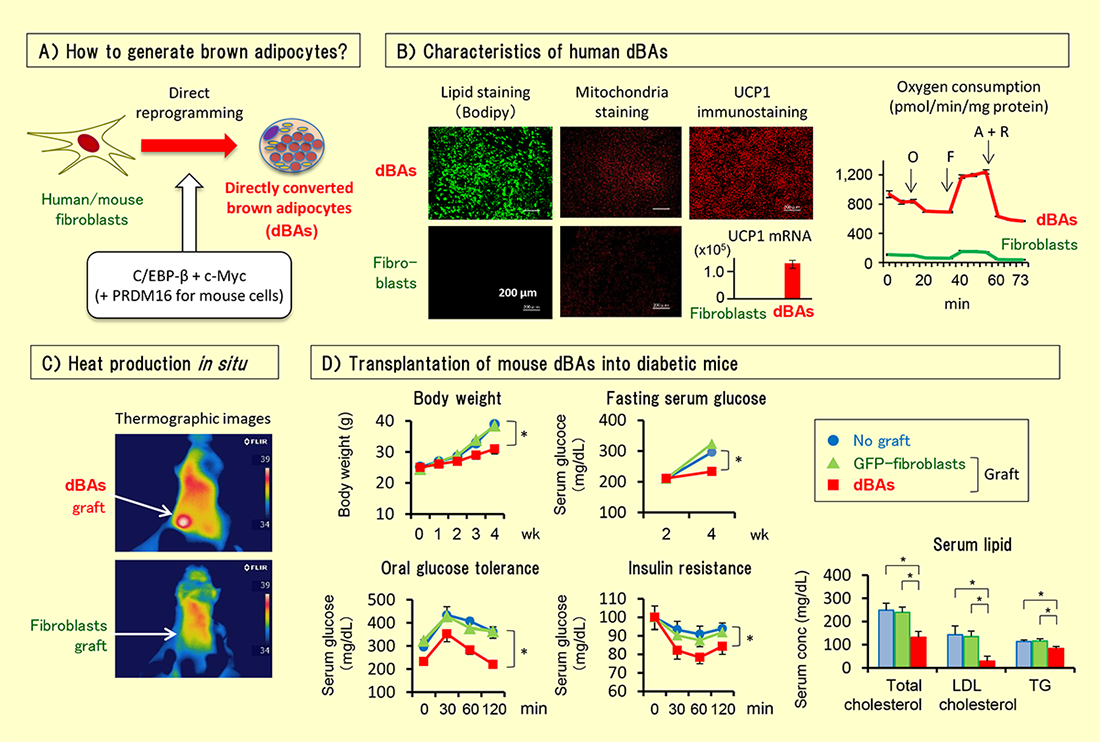
褐色脂肪細胞は食物由来の余剰エネルギーを散逸する細胞であるが、糖尿病患者ではその機能はほとんど消失している。我々は、ヒトとマウスの線維芽細胞を直接、機能的な褐色脂肪細胞にリプログラミングする技術を樹立した。
その効率は90%以上であり、得られた褐色脂肪細胞(dBAs)はUCP1を高発現し、高い代謝活性を有する。糖尿病マウスに移植すると、食餌量は変えずに、インスリン抵抗性、体重増加、耐糖能、脂質異常症がすべて抑制できる。そこで糖尿病に対する新しい再生医療をもたらすと考えられる(岸田他、Stem Cell Reports)。
Brown adipocytes dissipate excess energy originated from food as heat, while diabetic patients have mostly lost functional brown adipocytes. We established a technology to directly convert human and mouse fibroblasts into brown adipocytes at an efficiency of more than 90%. The directly converted brown adipocytes (dBAs) highly express UCP1 and have high metabolic activities. Transplantation of dBAs into diabetic mice significantly improved insulin resistance, body weight gain, glucose tolerance and dyslipidemia, without affecting food intake. This technology may generate novel regenerative therapy for diabetes (Kishida et al, Stem Cell Reports).
一部プロジェクトのご紹介 - See some projects among others -
- 新型コロナウイルス・オミクロン変異株に対する茶カテキン類の効果
Effects of tea catechin-related compounds on Omicron subvariants of SARS-CoV-2 - 腫瘍微小環境の低pHはプロトンセンサーGたんぱく共役レセプターをを介して腫瘍のPDL-1の発現を低下させる
Extracellular acidity in tumor tissue upregulates programmed cell death protein 1 expression on tumor cells via proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptors - 緑茶カテキン、カテキン誘導体、およびガレート型テアフラビンによる新型コロナウイルスの試験管内での有意な不活化;紅茶と緑茶による試験管内での唾液中の新型コロナウイルスの迅速な不活化
Significant Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by a Green Tea Catechin, a Catechin-derivative and Galloylated Theaflavins in vitro; Rapid Inactivation in vitro of SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva by Black Tea and Green Tea - 新規多孔性3Dスキャフォールドと直接誘導骨芽細胞を用いた骨再生
Nanogel tectonic porous 3D scaffold for direct reprogramming fibroblasts into osteoblasts and bone regeneration - TGFR阻害剤による骨芽細胞のケミカル・ダイレクト・リプログラミング
Chemical direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts into osteoblasts by a TGFR blockade - 筋芽細胞のダイレクト・リプログラミングと筋管形成
Direct reprogramming of functional myoblasts that are capable of forming multinuclear myotube - シュワン細胞のダイレクト・リプログラミングと末梢神経損傷の再生
Direct reprogramming of functional Schwann cells that promote regeneration of peripheral nerve - 褐色脂肪のダイレクト・リプログラミングと代謝疾患の制御
Direct reprogramming of functional brown adipocytes that control metabolic diseases - 骨芽細胞のダイレクト・リプログラミングと骨再生
Direct reprogramming of functional osteoblasts that regenerate bone tissue - IL-21 によるアレルギー応答の制御とその分子機構
IL-21-mediated regulation of allergic responses and its molecular mechanisms - IL-27 による NK 細胞活性化と ADCC を介した腫瘍抑制
IL-27 augments NK cytotoxicity and induces ADCC-based tumor suppression - EBV- エピゾーマルベクターによる外来遺伝子の高効率導入、高発現、長期間持続の機構解明
Mechanisms underlying the high-rate transfection, high-level expression, and long-term maintenance of exogenous genes mediated by the Epstein-Barr virus-based episomal vector - 細胞の分化と初期化に伴う染色体エピジェネティック修飾の解析
Analyses of epigenetic modification of chromosomes upon cell differentiation and reprogramming